# vee-cli脚手架实践(下)
# 前言
书接上回 vee-cli脚手架实践(中)
上回主要介绍了create.js脚本的模板选择与拉取,本篇旨在讲述选择对应模板后编译以及最后的npm发包
# 模板编译
# 依赖包
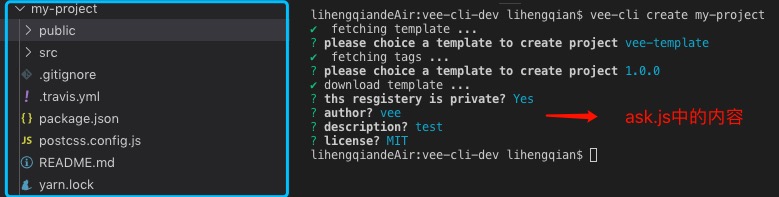
[包目录结构]
- metalsmith (用于遍历文件夹,判断是否需要进行模板渲染)
- consolidate (统一所有的模板引擎)
[目录描述] 对于有模板引擎渲染的仓库,一般会有一个ask.js,
module.exports = [
{
type: 'confirm',
name: 'private',
message: 'ths resgistery is private?',
},
{
type: 'input',
name: 'author',
message: 'author?',
},
{
type: 'input',
name: 'description',
message: 'description?',
},
{
type: 'input',
name: 'license',
message: 'license?',
},
]
与用户进行命令行交互后,将对应的内容动态注入到模板中,这里常用的模板引擎有ejs、handlebars等,consolidate将这里用到的引擎进行了统一,可以自由选择
# 逻辑代码
// 判断是否存在ask.js文件
if(!fs.existsSync(path.join(result, 'ask.js'))) {
// 直接下载
await ncpPro(result, path.resolve(projectName));
} else {
// 模板渲染后再拷贝
await new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
MetalSmith(__dirname)
.source(result)
.destination(path.resolve(projectName))
.use(async (files, metal, done) => {
const a = require(path.join(result, 'ask.js'));
const r = await Inquirer.prompt(a);
const m = metal.metadata();
Object.assign(m, r);
delete files['ask.js'];
done()
})
.use((files, metal, done) => {
const meta = metal.metadata();
Object.keys(files).forEach(async (file) => {
let c = files[file].contents.toString();
// 只有js和json文件才去做处理
if(file.includes('js') || file.includes('json')) {
// 判断是否是模板 可用正则匹配
if(c.includes('<%')) {
c = await renderPro(c, meta);
files[file].contents = Buffer.from(c);
}
}
})
done()
})
.build((err) => {
if(err) {
reject()
} else {
resolve()
}
})
})
}
这里主要是对之前直接down仓库内容复制做了扩展,判断是否需要进行模板编译,也就是用户是否需要再次输入内容,动态的注入到拉取的模板中,这里还可以选择更多的其他配置,但大致原理基本一致,具体详细的可以参看vue-cli源码,其中对其他部分也做了更为详尽的扩展
# 相关包源码分析
# metalsmith
var assert = require('assert')
var clone = require('clone')
var fs = require('co-fs-extra')
var matter = require('gray-matter')
var Mode = require('stat-mode')
var path = require('path')
var readdir = require('recursive-readdir')
var rm = require('rimraf')
var thunkify = require('thunkify')
var unyield = require('unyield')
var utf8 = require('is-utf8')
var Ware = require('ware')
readdir = thunkify(readdir)
rm = thunkify(rm)
var isBoolean = function(b) {return typeof b === 'boolean'}
var isNumber = function(n) {return typeof n === 'number' && !Number.isNaN(n)}
var isObject = function(o) {return o !== null && typeof o === 'object'}
var isString = function(s) {return typeof s === 'string'}
module.exports = Metalsmith
function Metalsmith(directory){
if (!(this instanceof Metalsmith)) return new Metalsmith(directory)
assert(directory, 'You must pass a working directory path.')
this.plugins = []
this.ignores = []
this.directory(directory)
this.metadata({})
this.source('src')
this.destination('build')
this.concurrency(Infinity)
this.clean(true)
this.frontmatter(true)
}
Metalsmith.prototype.use = function(plugin){
this.plugins.push(plugin)
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.directory = function(directory){
if (!arguments.length) return path.resolve(this._directory)
assert(isString(directory), 'You must pass a directory path string.')
this._directory = directory
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.metadata = function(metadata){
if (!arguments.length) return this._metadata
assert(isObject(metadata), 'You must pass a metadata object.')
this._metadata = clone(metadata)
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.source = function(path){
if (!arguments.length) return this.path(this._source)
assert(isString(path), 'You must pass a source path string.')
this._source = path
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.destination = function(path){
if (!arguments.length) return this.path(this._destination)
assert(isString(path), 'You must pass a destination path string.')
this._destination = path
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.concurrency = function(max){
if (!arguments.length) return this._concurrency
assert(isNumber(max), 'You must pass a number for concurrency.')
this._concurrency = max
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.clean = function(clean){
if (!arguments.length) return this._clean
assert(isBoolean(clean), 'You must pass a boolean.')
this._clean = clean
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.frontmatter = function(frontmatter){
if (!arguments.length) return this._frontmatter
assert(isBoolean(frontmatter), 'You must pass a boolean.')
this._frontmatter = frontmatter
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.ignore = function(files){
if (!arguments.length) return this.ignores.slice()
this.ignores = this.ignores.concat(files)
return this
}
Metalsmith.prototype.path = function(){
var paths = [].slice.call(arguments)
paths.unshift(this.directory())
return path.resolve.apply(path, paths)
}
Metalsmith.prototype.build = unyield(function*(){
var clean = this.clean()
var dest = this.destination()
if (clean) yield rm(path.join(dest, '*'), { glob: { dot: true } })
var files = yield this.process()
yield this.write(files)
return files
})
Metalsmith.prototype.process = unyield(function*(){
var files = yield this.read()
files = yield this.run(files)
return files
})
Metalsmith.prototype.run = unyield(function*(files, plugins){
var ware = new Ware(plugins || this.plugins)
var run = thunkify(ware.run.bind(ware))
var res = yield run(files, this)
return res[0]
})
Metalsmith.prototype.read = unyield(function*(dir){
dir = dir || this.source()
var read = this.readFile.bind(this)
var concurrency = this.concurrency()
var ignores = this.ignores || null
var paths = yield readdir(dir, ignores)
var files = []
var complete = 0
var batch
while (complete < paths.length) {
batch = paths.slice(complete, complete + concurrency)
batch = yield batch.map(read)
files = files.concat(batch)
complete += concurrency
}
return paths.reduce(memoizer, {})
function memoizer(memo, file, i) {
file = path.relative(dir, file)
memo[file] = files[i]
return memo
}
})
Metalsmith.prototype.readFile = unyield(function*(file){
var src = this.source()
var ret = {}
if (!path.isAbsolute(file)) file = path.resolve(src, file)
try {
var frontmatter = this.frontmatter()
var stats = yield fs.stat(file)
var buffer = yield fs.readFile(file)
var parsed
if (frontmatter && utf8(buffer)) {
try {
parsed = matter(buffer.toString())
} catch (e) {
var err = new Error('Invalid frontmatter in the file at: ' + file)
err.code = 'invalid_frontmatter'
throw err
}
ret = parsed.data
ret.contents = (Buffer.hasOwnProperty('from'))
? Buffer.from(parsed.content)
: new Buffer(parsed.content)
} else {
ret.contents = buffer
}
ret.mode = Mode(stats).toOctal()
ret.stats = stats
} catch (e) {
if (e.code == 'invalid_frontmatter') throw e
e.message = 'Failed to read the file at: ' + file + '\n\n' + e.message
e.code = 'failed_read'
throw e
}
return ret
})
Metalsmith.prototype.write = unyield(function*(files, dir){
dir = dir || this.destination()
var write = this.writeFile.bind(this)
var concurrency = this.concurrency()
var keys = Object.keys(files)
var complete = 0
var batch
while (complete < keys.length) {
batch = keys.slice(complete, complete + concurrency)
yield batch.map(writer)
complete += concurrency
}
function writer(key){
var file = path.resolve(dir, key)
return write(file, files[key])
}
})
Metalsmith.prototype.writeFile = unyield(function*(file, data){
var dest = this.destination()
if (!path.isAbsolute(file)) file = path.resolve(dest, file)
try {
yield fs.outputFile(file, data.contents)
if (data.mode) yield fs.chmod(file, data.mode)
} catch (e) {
e.message = 'Failed to write the file at: ' + file + '\n\n' + e.message
throw e
}
})
metalsmith用的是挂在原型上的写法,通过插件的链式传递方法进行数据的透传,属于原型设计模式的应用,对于js来说原型模式是天生存在的,因而对于希望通过链式传递且写法且变量不多的小型库而言,这种方式不失为一种好的方法,对链式调用有兴趣的同学可以研究下jQuery源码及koa源码,虽然大型库组织不是一种模式的展现,但是其中小部分还是有异曲同工的地方的,对于链式调用的实现方法也可以有一个横向的扩展和对比
# consolidate
consolidate主要是对不同模板引擎的选择分发,这里挑选了最核心的几个功能函数
function cache(options, compiled) {
if (compiled && options.filename && options.cache) {
delete readCache[options.filename];
cacheStore[options.filename] = compiled;
return compiled;
}
if (options.filename && options.cache) {
return cacheStore[options.filename];
}
return compiled;
}
function read(path, options, cb) {
var str = readCache[path];
var cached = options.cache && str && typeof str === 'string';
if (cached) return cb(null, str);
fs.readFile(path, 'utf8', function(err, str) {
if (err) return cb(err);
str = str.replace(/^\uFEFF/, '');
if (options.cache) readCache[path] = str;
cb(null, str);
});
}
function readPartials(path, options, cb) {
if (!options.partials) return cb();
var keys = Object.keys(options.partials);
var partials = {};
function next(index) {
if (index === keys.length) return cb(null, partials);
var key = keys[index];
var partialPath = options.partials[key];
if (partialPath === undefined || partialPath === null || partialPath === false) {
return next(++index);
}
var file;
if (isAbsolute(partialPath)) {
if (extname(partialPath) !== '') {
file = partialPath;
} else {
file = join(partialPath + extname(path));
}
} else {
file = join(dirname(path), partialPath + extname(path));
}
read(file, options, function(err, str) {
if (err) return cb(err);
partials[key] = str;
next(++index);
});
}
next(0);
}
function fromStringRenderer(name) {
return function(path, options, cb) {
options.filename = path;
return promisify(cb, function(cb) {
readPartials(path, options, function(err, partials) {
var extend = (requires.extend || (requires.extend = require('util')._extend));
var opts = extend({}, options);
opts.partials = partials;
if (err) return cb(err);
if (cache(opts)) {
exports[name].render('', opts, cb);
} else {
read(path, opts, function(err, str) {
if (err) return cb(err);
exports[name].render(str, opts, cb);
});
}
});
});
};
}
consolidate这个库也是tj大佬写的,其主要思路是通过读取[read]对应文件里的字符[readPartials]获取到需要的字符后对字符进行查找对应名称[fromStringRenderer]的渲染,其中读取过程做了[cache]优化,剩下的就是对对应的模板渲染引擎的分发,从而做到了汇聚分发的效果,整体思路还是很明确的,另外多说一句,tj大佬似乎对类生成器函数处理有种蜜汁喜爱,各种库都有它的影子,对生成器方式处理感兴趣的同学,可以参考co库源码
# 发包
# 连接npm
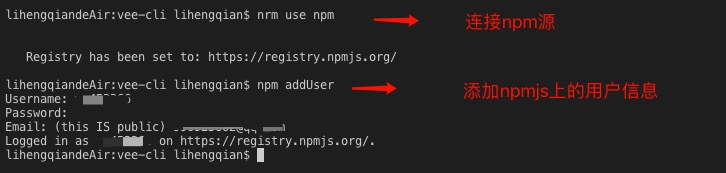
连接npm源(如果没有nrm,需要npm i nrm -g) => 填写npm官网的个人用户信息
# 发布到npm
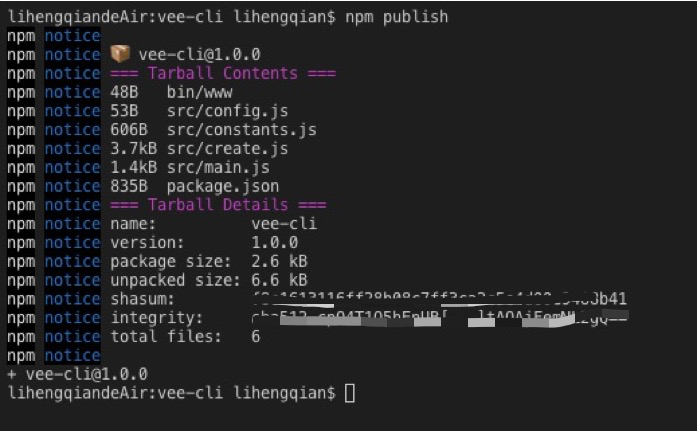
对于整个npm发包等感兴趣的同学,可以参考npm文档,也可以参考这篇文章npm包的发布与删除
# 验证
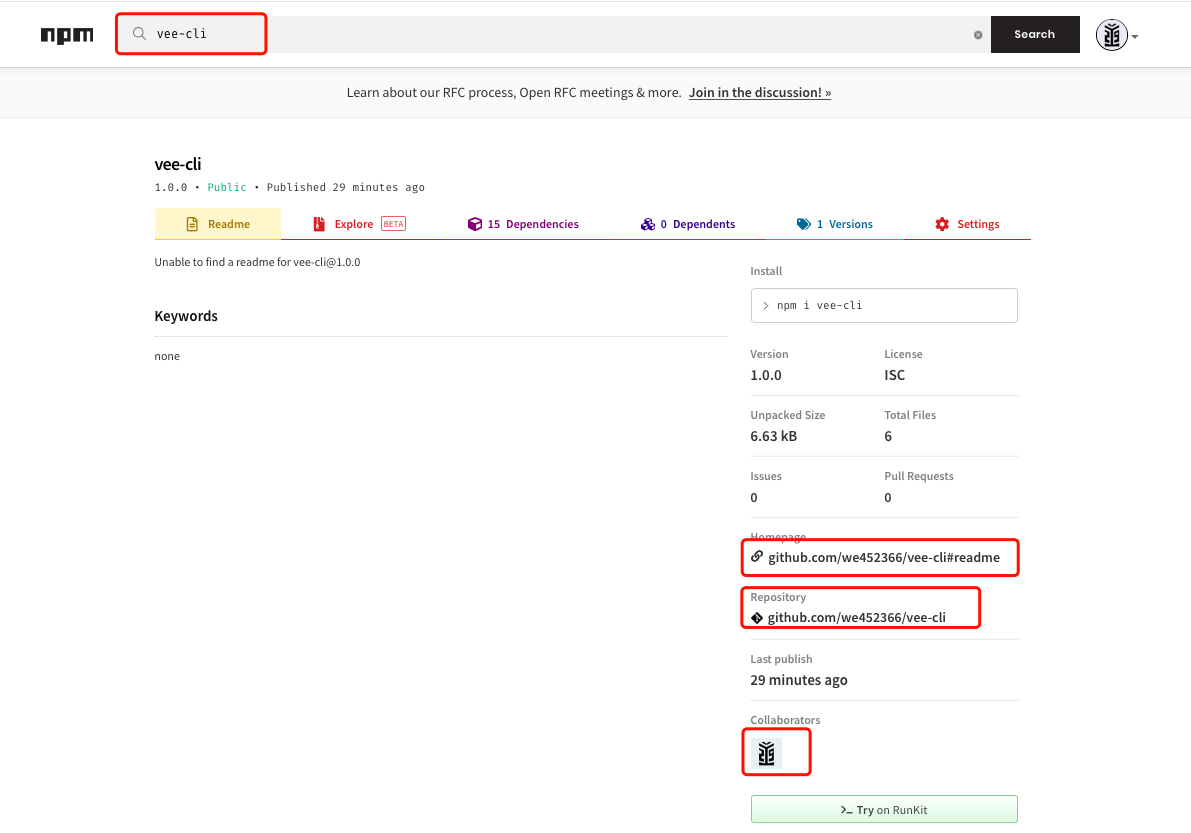
搜索npmjs官网上,可以查找到,npm unlink后或换一台机器,可以npm i vee-cli进行包下载,这样一个脚手架的发包就完成了
# 总结
脚手架是前端工程化领域的基本项,个人认为掌握前端脚手架的开发是十分重要的,这三篇内容 vee-cli脚手架实践(上) vee-cli脚手架实践(中) vee-cli脚手架实践(下) 旨在提供一个大概思路及样板,目前只包含了
1、命令行;2、模板拉取;
,其相对于成熟的脚手架如vue-cli、create-react-app、@angular/cli等来说,还有很多很多工作要做,包括
3、本地服务;4、打包构建;5、集成部署;6、周边其他
等都还需要完善,想要在工程化领域有所建树的同学,不妨在这几个方面多下下功夫
TIP